Wayne Tham's Coding Projects
Hi, My name is Wayne! Learning robotics has taught me how to think creatively and logically to solve real-world problems. After robotics, I had sparked an interest in learning text-based coding in Python. It was great to learn how to use Python to solve math problems and other more complex ones by issuing instructions. I also wanted to learn beyond just regular Python programs and so I started picking up PyGame. It lets me learn how to make different kinds of games for my friends and I to play. It made me realise that making games to connect with friends can be both an enriching and fun experience.
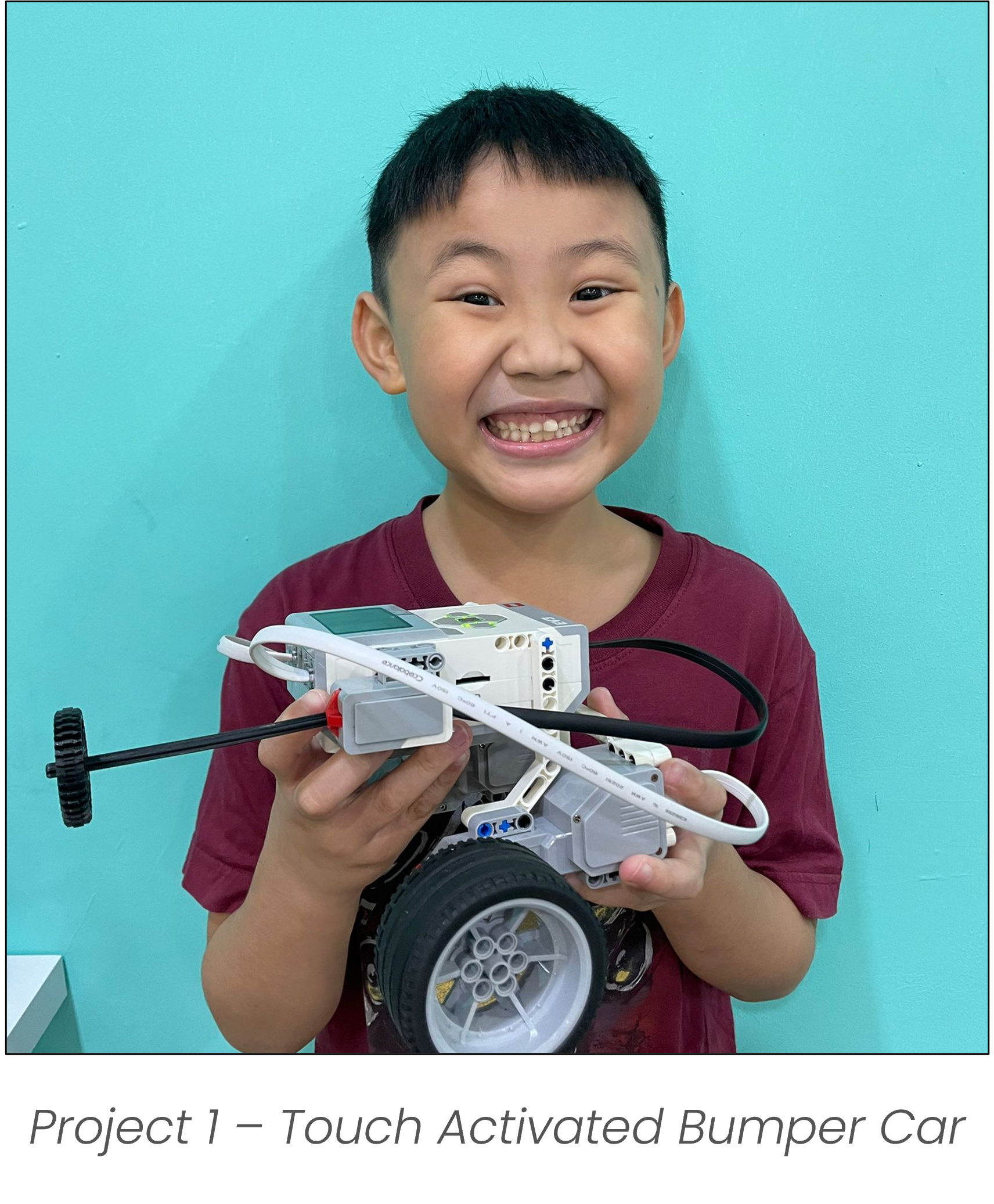
Touch Activated Bumper Car
I learnt how to use the LEGO technic parts to create different designs. By applying coding concepts such as conditionals (if-else) and integrating various sensors, I programmed my creations to respond dynamically to their environment. One example was a bumper car that automatically reverses when its front touch sensor detects a collision—mimicking real-world applications of obstacle detection used in autonomous vehicles and robotic systems to enhance safety and navigation.


Colour Activated Sushi Belt
Using an ultrasonic sensor, I recreated a sushi belt that moves only if the colour sensor detects a specific colour!
2 Sensor Coin Dispenser
Inspired by arcade coin dispensers, I applied the design principles and coding skills I learned to build a distance-activated coin dispenser. The dispenser uses two ultrasonic sensors that detect my hand in a specific sequence within a defined distance threshold. When both sensors are triggered in order, the mechanism opens to release coins. This project demonstrates how sensor integration and conditional logic can create automated systems, similar to those used in vending machines.
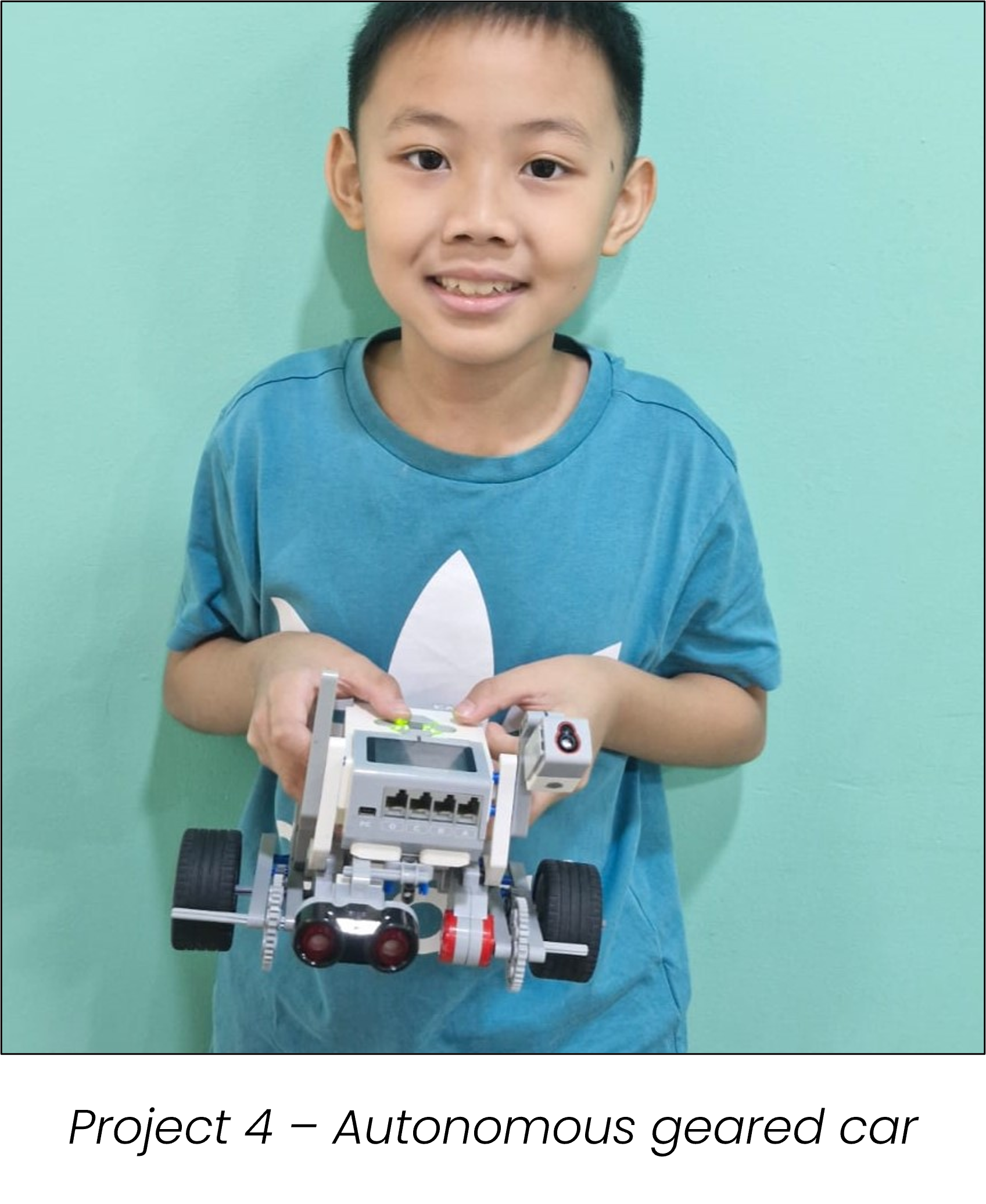

Colour and ultrasonic automated car
I decided to create an automated car using LEGO Technic parts that can return to its original parking position after detecting an obstacle. This project simulates the logic behind autonomous parking systems found in modern vehicles. Using the concept of nested while loops with variables, I programmed the car to activate and begin moving when the colour sensor detects a specific colour. While in motion, the car continuously checks for obstacles using the ultrasonic sensor. Once an obstacle is detected, the car automatically stops and reverses back to its starting point—mimicking a vehicle returning to its parking spot. This entire process repeats endlessly, creating a looped simulation of real-world automated vehicle behavior.
Description:
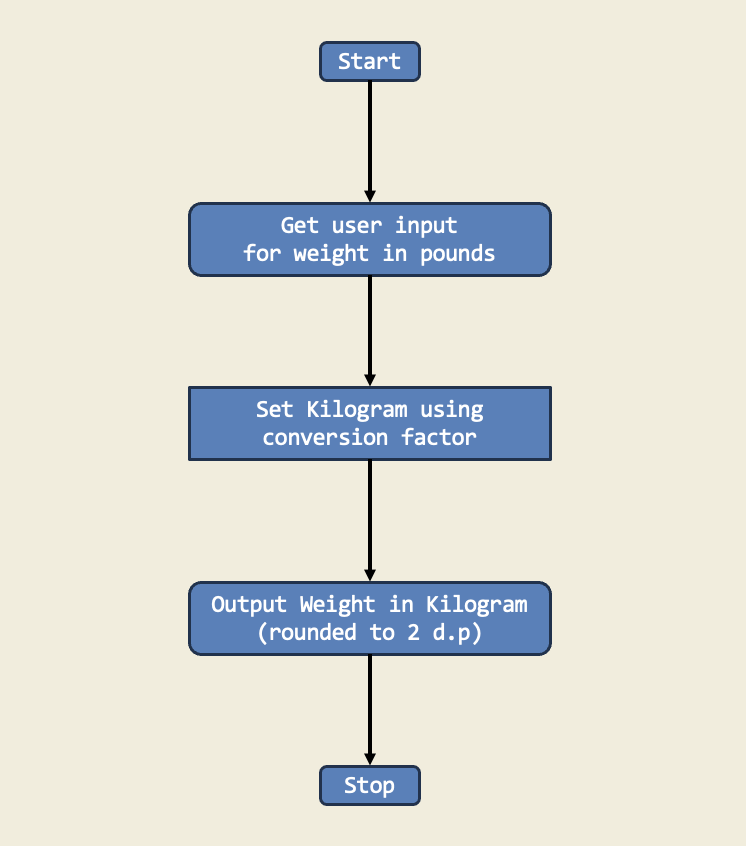
In this project, I learned how to convert weight from pounds to kilograms by multiplying by a conversion factor. This is important because it teaches us how to change one unit of measurement to another so we can compare different types of data.
Diagram:
Trinket:
Description:
In this project, I designed a program that checks if a number is even or odd using if-else statements. This project teaches me how to make decisions in code based on conditions.
Diagram:
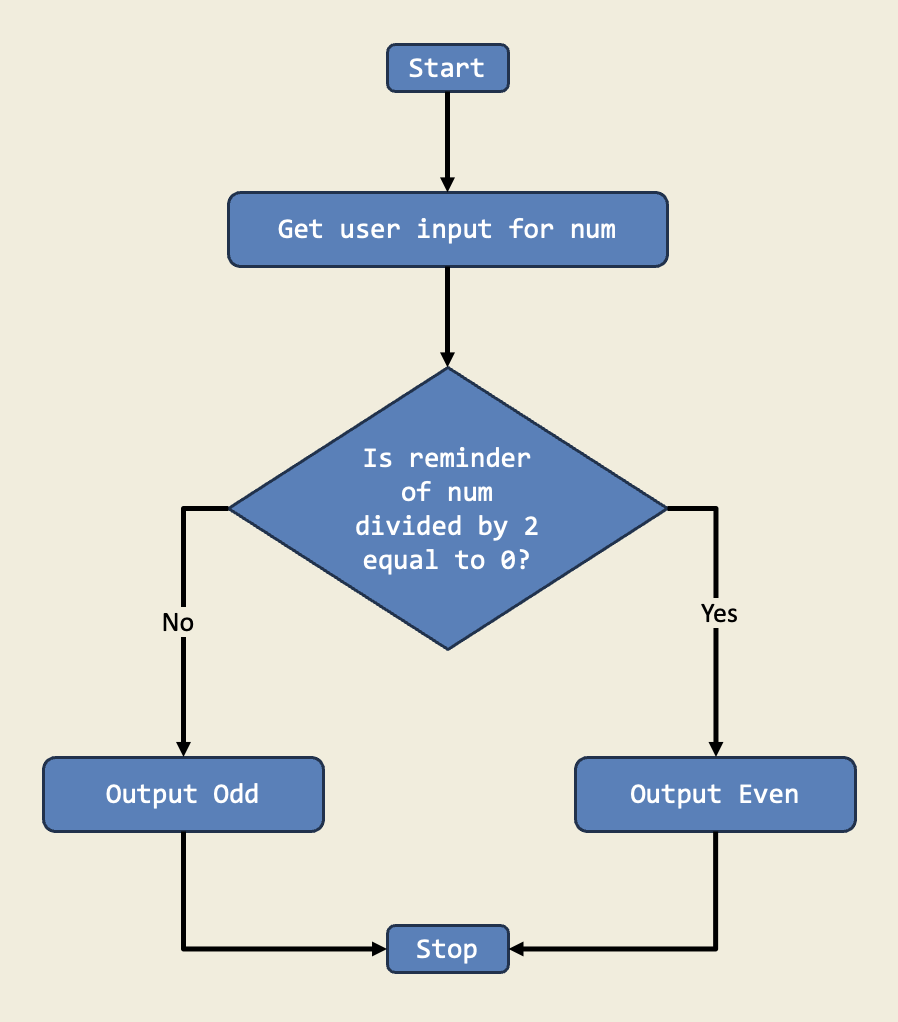
Trinket:
Description:
In this project, I created a number pyramid using nested for loops. The outer loop controls the number of rows, while the inner loop prints the numbers in each row. This project demonstrates how to use loops to create patterns and shapes in Python.
Diagram:
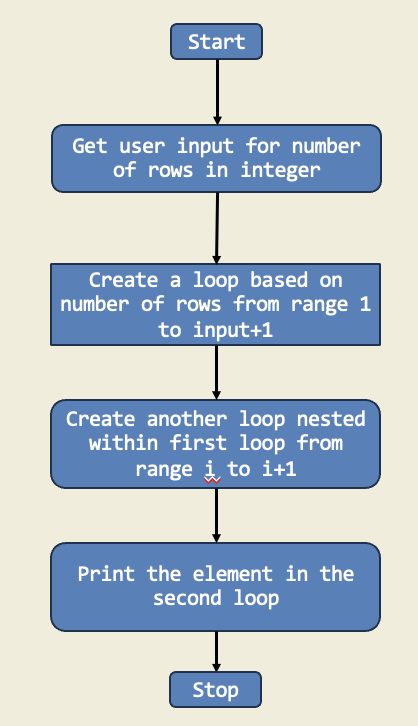
Trinket:
Description:
In this project, I managed a store's inventory that increased daily using a for loop. I calculated the number of units on day 15 and the total after 15 days. This is important because it shows how for loops help us perform repetitive tasks easily.
Diagram:
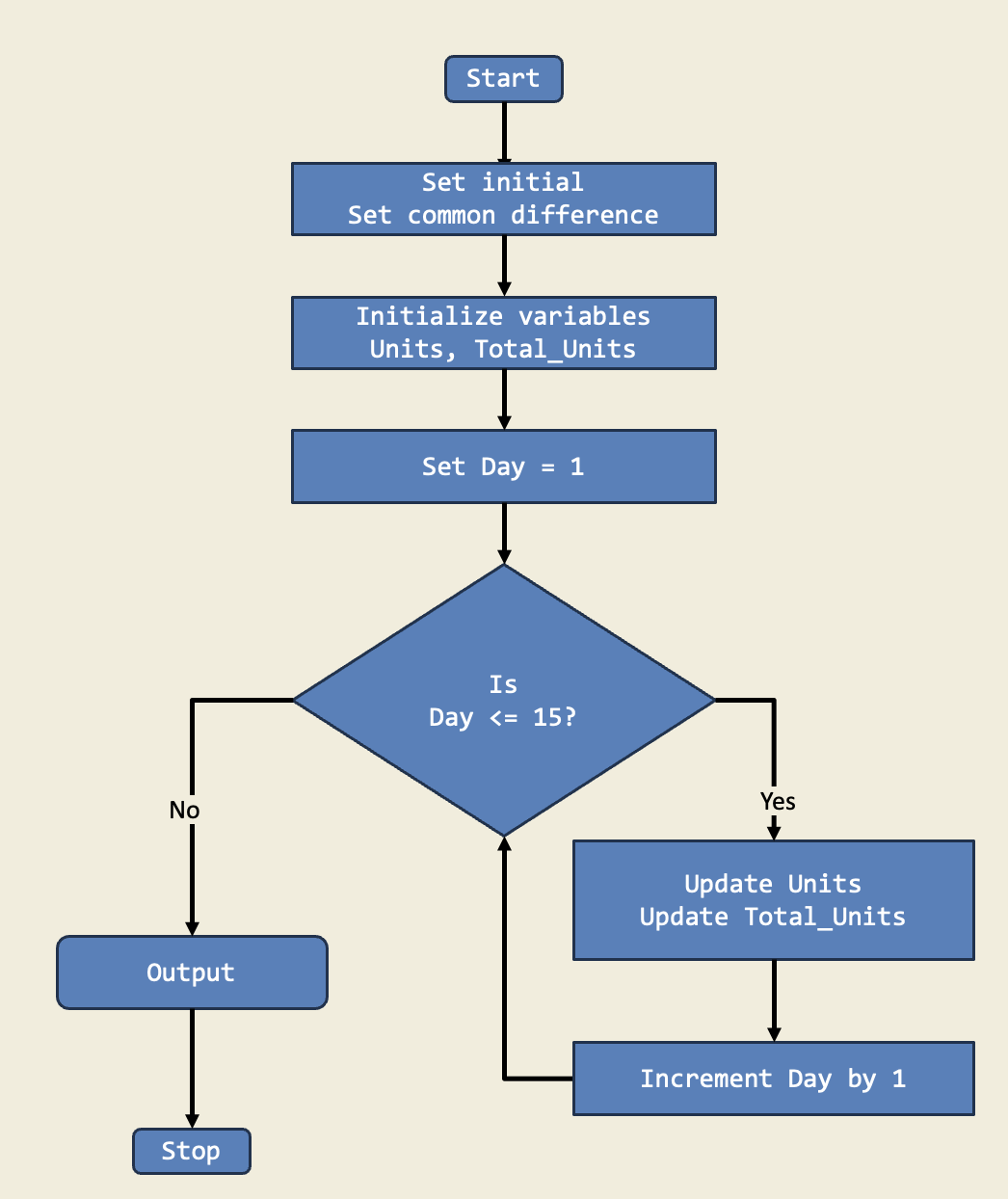
Trinket:
Description:
This game challenges you to decide if a number is prime by using if-else statements. It’s a fun way to reinforce the concept of prime numbers and divisibility in code.
Diagram:
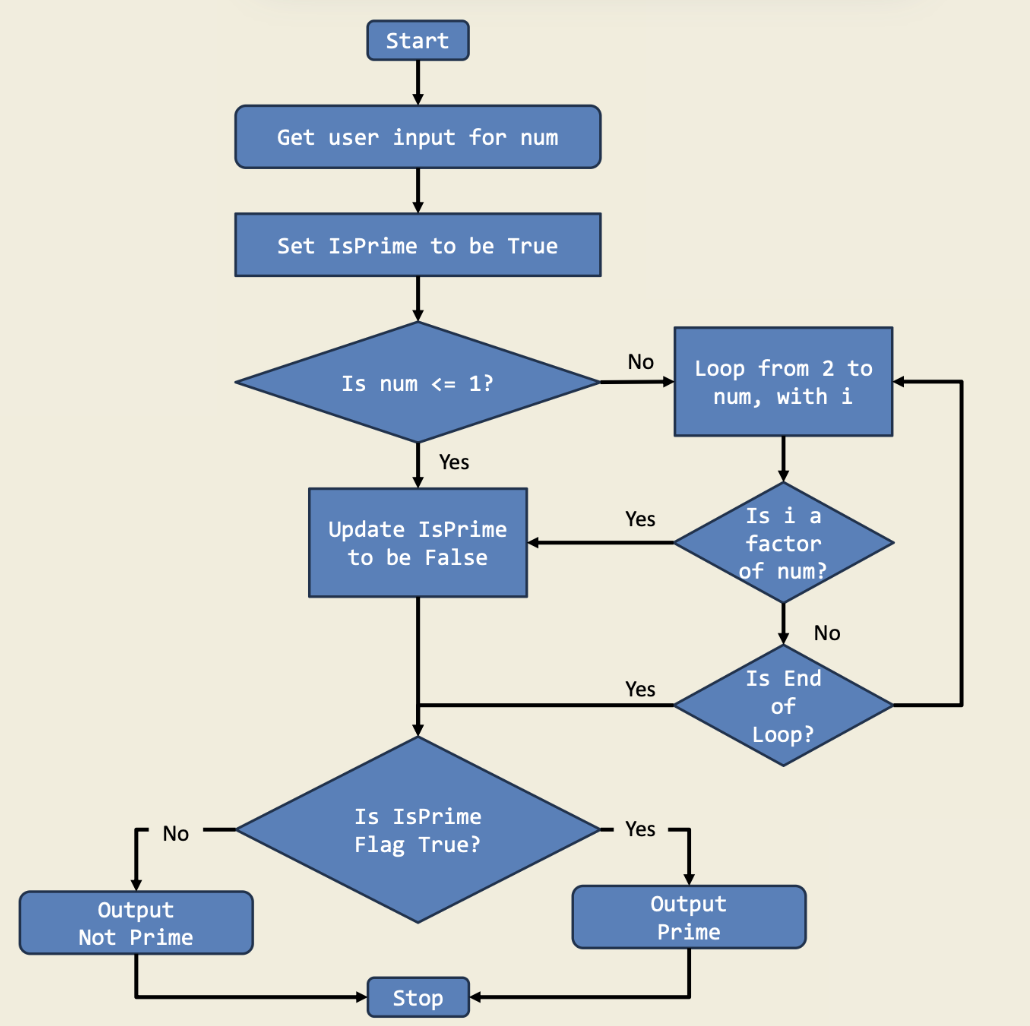
Trinket:
Description:
In a word game, players needed to determine whether two words were anagrams or not. I created a Python program named anagram_checker.py that takes in two user inputs for words and checked if the provided words were anagrams. An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
Diagram:
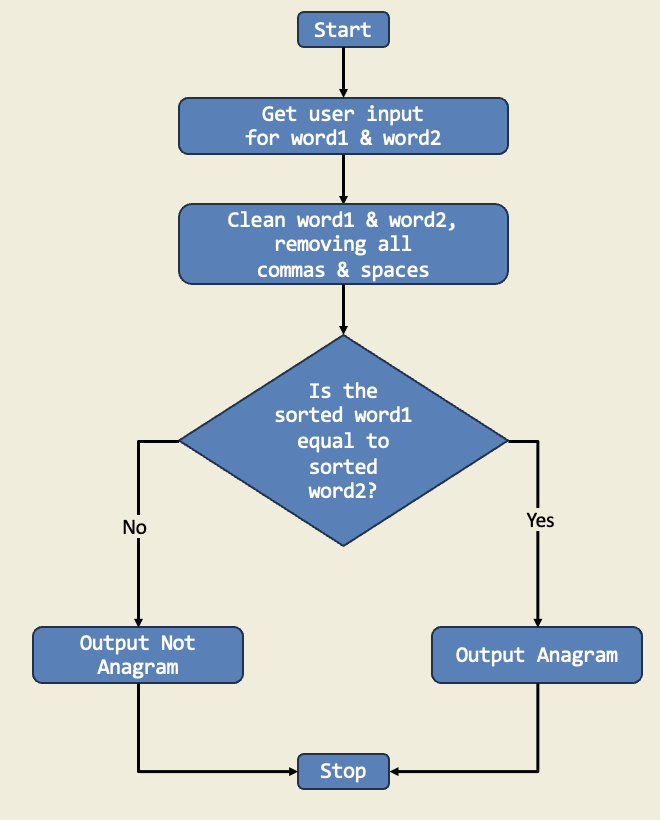
Trinket:
Description:
In this project, I built a countdown timer that uses a while loop to count down from a starting number until it reaches 1. This is important because it shows me how to repeat an action until a condition is met.
Diagram:
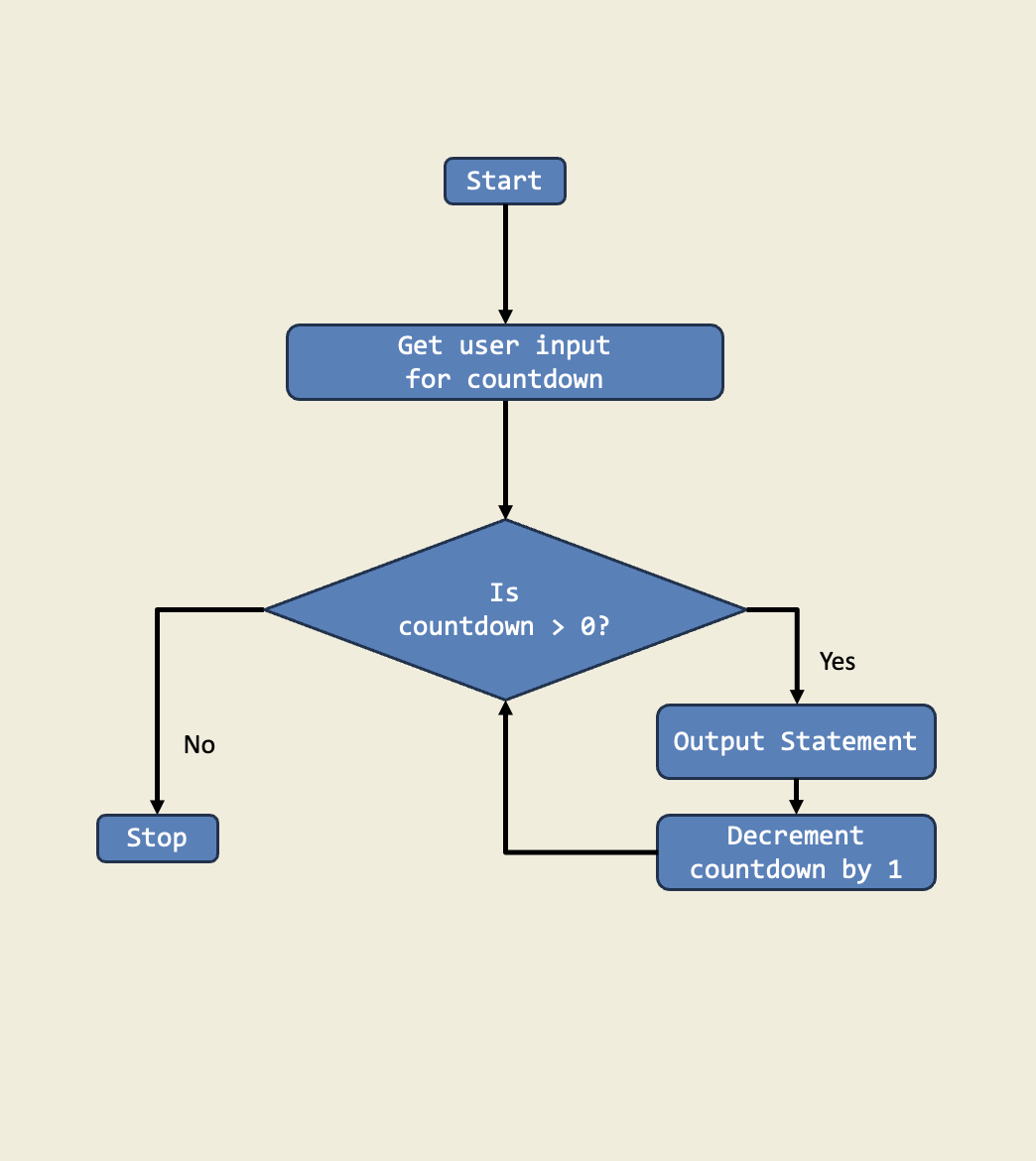
Trinket:
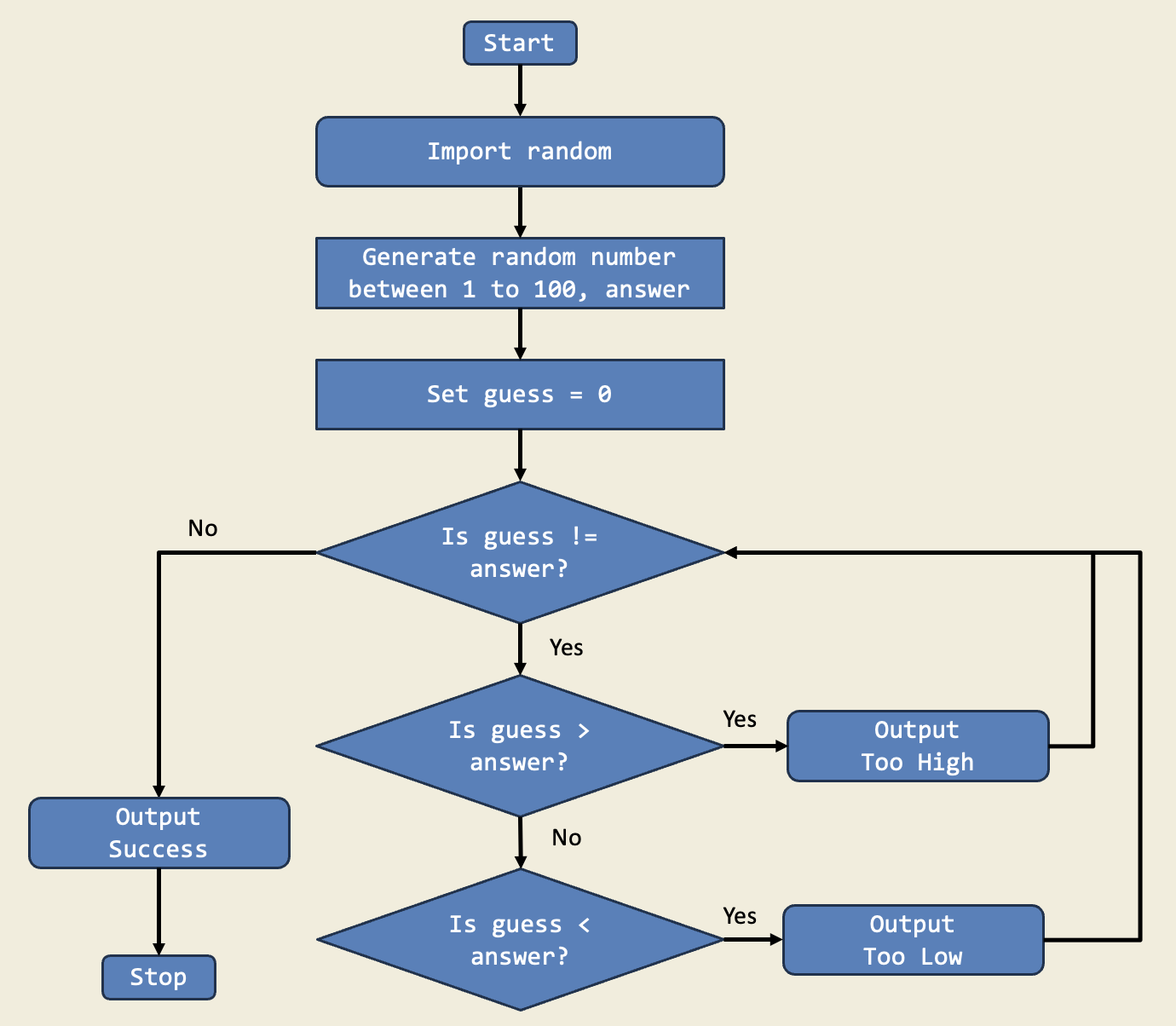
Description:
In this project, I built a guessing game using a while loop that keeps asking for a guess until the answer is right. The game tells me if my guess is too high or too low. This is important because while loops let me repeat actions until a condition is met, which is perfect for games.
Diagram: